Maintaining a healthy weight over the long term is one of the most common yet challenging health goals for people across all age groups. While short-term weight loss plans may show quick results, true success lies in sustainable habits that can be followed for years. The foundation of long-term weight management rests on two pillars: a balanced diet and regular exercise. Together, they not only help manage body weight but also improve overall physical, mental, and metabolic health.
In today’s fast-paced lifestyle—especially in growing urban regions where work stress and sedentary routines are common—understanding how diet and exercise work together becomes even more important.
Understanding Long-Term Weight Management
Long-term weight management is not about extreme dieting or intense workout routines followed for a few weeks. Instead, it focuses on maintaining a healthy body weight by creating a consistent energy balance—where the calories consumed through food align with the calories burned through daily activity and exercise.
Unlike crash diets that often lead to weight regain, sustainable weight management emphasizes gradual changes, mindful eating, and an active lifestyle. This approach reduces the risk of lifestyle diseases such as diabetes, heart disease, and joint problems while enhancing quality of life.
The Role of Diet in Long-Term Weight Management
Diet plays a crucial role in determining body weight because food intake directly influences calorie consumption, metabolism, and nutrient balance.
1. Balanced Nutrition Over Restrictive Diets
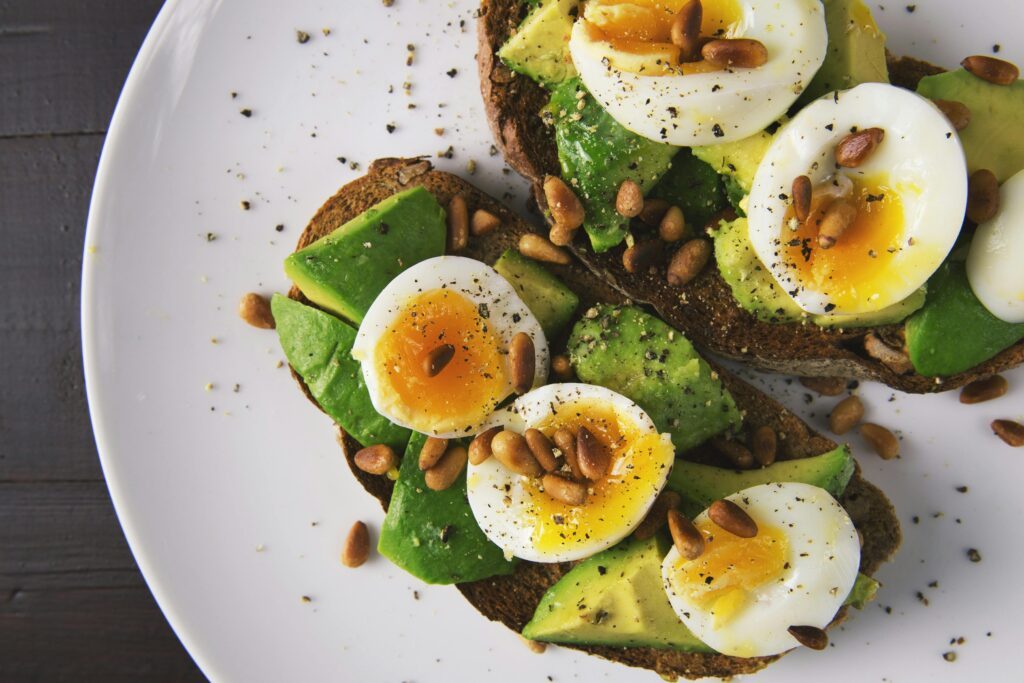
A healthy diet should include the right proportion of macronutrients—carbohydrates, proteins, and fats—along with essential vitamins and minerals. Restrictive diets that eliminate entire food groups often lead to nutrient deficiencies and are difficult to sustain.
Instead, long-term success comes from balanced meals that provide energy, support metabolism, and keep hunger under control.
2. Importance of Portion Control
Even healthy foods can contribute to weight gain if consumed in excess. Learning portion control helps regulate calorie intake without feeling deprived. Using smaller plates, eating slowly, and listening to hunger cues are practical strategies for maintaining portions.
3. Protein for Satiety and Muscle Health
Protein-rich foods such as pulses, eggs, lean meats, dairy, and plant-based sources help increase satiety and preserve muscle mass. Higher protein intake supports metabolism and reduces cravings, making it easier to stick to a healthy eating plan.
4. Role of Fiber and Whole Foods
Fiber-rich foods like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes improve digestion and promote fullness. These foods are less calorie-dense and help prevent overeating. Choosing whole foods over processed items significantly supports long-term weight control.
5. Sustainable Eating Habits
Consistency matters more than perfection. Occasional indulgences are normal, but the focus should remain on overall eating patterns rather than single meals. Sustainable habits, such as home-cooked meals and mindful grocery shopping, contribute to lasting results.
The Role of Exercise in Long-Term Weight Management
While diet largely determines calorie intake, exercise plays a vital role in calorie expenditure, muscle maintenance, and metabolic health.
1. Boosting Metabolism
Regular physical activity increases metabolic rate, allowing the body to burn more calories even at rest. Strength training, in particular, helps build muscle, which is more metabolically active than fat.
2. Fat Loss and Muscle Preservation
Exercise helps ensure that weight loss comes primarily from fat rather than muscle. This is crucial for maintaining strength, posture, and long-term metabolic health.
3. Types of Exercise for Weight Management
-
Cardiovascular exercises like walking, cycling, swimming, and jogging improve heart health and burn calories.
-
Strength training helps tone muscles and improves body composition.
-
Flexibility and mobility exercises such as yoga and stretching support recovery and prevent injuries.
A combination of these forms yields the best long-term results.
4. Mental Health Benefits
Exercise reduces stress, anxiety, and emotional eating—common barriers to weight management. Regular workouts release endorphins that improve mood and motivation, making it easier to maintain healthy habits.
5. Building an Active Lifestyle
Beyond structured workouts, daily activities such as taking stairs, walking short distances, or staying active at work significantly contribute to overall energy expenditure.
Why Diet and Exercise Must Work Together
Diet and exercise are most effective when combined. Relying on diet alone may lead to muscle loss, while exercise without proper nutrition may result in fatigue and inconsistent progress.
Together, they:
-
Create a healthy calorie balance
-
Improve body composition
-
Enhance metabolic efficiency
-
Support mental and emotional well-being
Long-term weight management is not a temporary phase but a lifestyle shift that integrates both nutrition and movement into daily life.
Urban Lifestyle, Wellness, and Modern Living
As cities expand and lifestyles evolve, access to wellness-focused environments becomes increasingly important. Residential developments that promote active living—through green spaces, walking tracks, gyms, and yoga zones—naturally encourage healthier habits. In this context, Pune Realty has been instrumental in shaping communities that support balanced living by integrating modern infrastructure with wellness-oriented design.
Such environments make it easier for individuals and families to stay active, manage stress, and prioritize health alongside professional commitments.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
-
Over-reliance on fad diets that promise quick results
-
Ignoring strength training and focusing only on cardio
-
Inconsistency in diet or exercise routines
-
Unrealistic expectations leading to frustration and dropouts
Awareness of these pitfalls helps build a more sustainable approach.
Tips for Sustainable Long-Term Success
-
Set realistic and measurable goals
-
Focus on habit-building rather than quick fixes
-
Track progress beyond the scale, such as energy levels and fitness
-
Stay flexible and adjust routines as needed
-
Prioritize sleep and stress management alongside diet and exercise
Conclusion
The role of diet and exercise in long-term weight management cannot be overstated. While diet controls what enters the body, exercise determines how efficiently the body uses that energy. Together, they form a powerful combination that supports not only healthy weight but also overall well-being.