Ranks Rocket Now Become Paid
Get Powerful Backlinks We having 20K+ Monthly Traffic with 35+ DA & 30+ PA
We value your privacy
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience, serve personalized ads or content, and analyze our traffic. By clicking "Accept All", you consent to our use of cookies.
We use cookies to help you navigate efficiently and perform certain functions. You will find detailed information about all cookies under each consent category below.
The cookies that are categorized as "Necessary" are stored on your browser as they are essential for enabling the basic functionalities of the site. ...
Necessary cookies are required to enable the basic features of this site, such as providing secure log-in or adjusting your consent preferences. These cookies do not store any personally identifiable data.
No cookies to display.
Functional cookies help perform certain functionalities like sharing the content of the website on social media platforms, collecting feedback, and other third-party features.
No cookies to display.
Analytical cookies are used to understand how visitors interact with the website. These cookies help provide information on metrics such as the number of visitors, bounce rate, traffic source, etc.
No cookies to display.
Performance cookies are used to understand and analyze the key performance indexes of the website which helps in delivering a better user experience for the visitors.
No cookies to display.
Advertisement cookies are used to provide visitors with customized advertisements based on the pages you visited previously and to analyze the effectiveness of the ad campaigns.
No cookies to display.
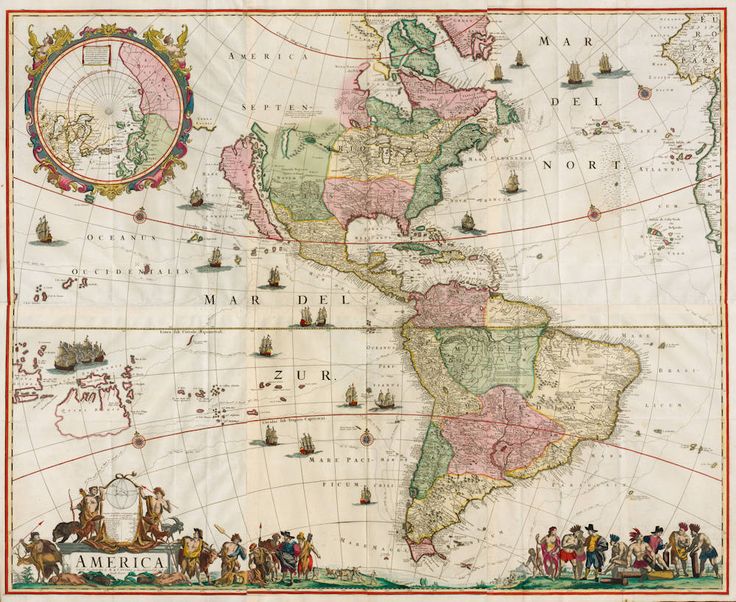
Reputable auction houses like Sotheby’s and Christie’s often feature rare and valuable maps in their sales. Specialized dealers with expertise in antique maps can provide valuable insights and authentication services.

Cornelius Wrecking offers comprehensive demolition services for any form of demolition. We handle interior and exterior demolition jobs, as well as excavation work for commercial, residential, and industrial sites. Commercial Demolition, Asbestos Abatement, Site Clearing, Ground Leveling, Site Prep, Earth Moving, Dump Trucking, Industrial Demolition, Residential Demolition, Land Clearing, Dirt Work, Asbestos Removal, Concrete Tear Out, Asphalt Tear Out, Excavating, and Other Services Being the best is not simple, but Cornelius Wrecking’s emphasis on safety, efficiency, and honesty has helped it become the preeminent demolition firm in Northwest Missouri.

Stay in the UK with Discretionary Leave to Remain from Immigration Solicitors4me

In the realm of electrical systems, where efficiency, safety, and reliability are paramount, the quality of every component plays a critical role. One such component, often overlooked but vitally important,
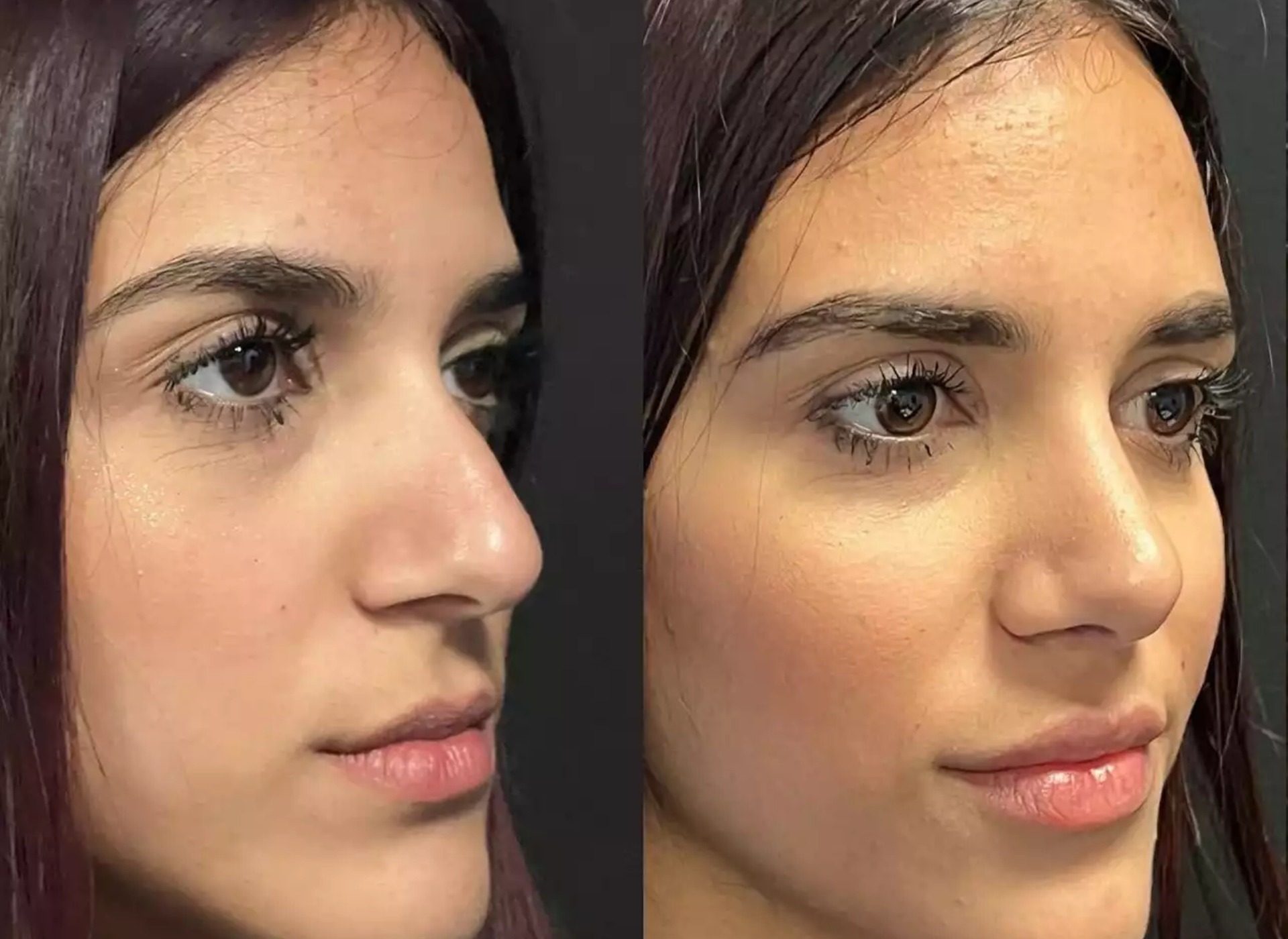

For those requiring revision procedures, selecting the best septoplasty surgeon in Dubai is essential to achieving the desired results and minimizing complications.

Market Overview: The sportswear market is experiencing rapid growth, driven by athleisure dominance, sustainability focus, digital integration. According to IMARC Group's latest research publication, "Sportswear Market Report by Product (Shoes, Clothes),

Broken Plant Market hoodies bring a fresh take on urban fashion, blending streetwear aesthetics with nature-inspired elements.

Upgrade your style with Burberry sunglasses designed for elegance and comfort. Whether you need Burberry sunglasses for men or Burberry sunglasses for women, find the perfect pair to complement your look. Explore classic aviators, oversized frames, and sleek rectangular designs, all crafted with premium materials. Check out the latest Burberry sunglasses price in India and shop authentic luxury eyewear online.

Discover how Shopify Plus API unlocks advanced development possibilities, enabling businesses to scale efficiently with Shopify Plus Development Services.

Punarnava is a powerful Ayurvedic herb with several health benefits, but it should be used with caution. Understanding Boerhavia diffusa side effects, proper Punarnava dosage, and potential risks can help ensure its safe use. Always consult an Ayurvedic expert before incorporating it into your health routine to avoid any adverse effects.

Pavers block, also known as paving block, is a type of pre-cast concrete or stone unit used for surfacing driveways, walkways, patios, and roads.

At times, saving money feels like an enormous task to achieve. This is because you might have other plans to materialize with this money.

Discover why welding industrial supply companies and steel distributors in Las Vegas are crucial for businesses in construction, manufacturing, and beyond.

By focusing on high-quality materials, expert craftsmanship, and timeless design, 925 sterling silver turquoise jewelry continues to captivate and inspire jewelry lovers worldwide.
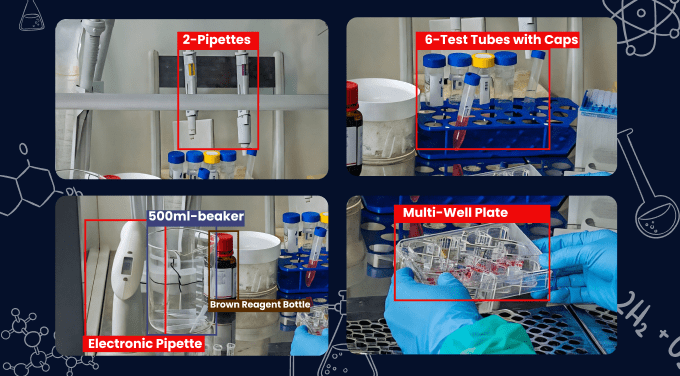
AI is increasingly spreading its wings into laboratory environments to improve efficiency and safety. As per the latest 2024 survey, more than 68% of laboratory professionals harness AI in their

The coconut sugar manufacturing plant report offers insights into the manufacturing process, financials, capital investment, expenses, ROI, and more for informed business decisions.

SEO is essential for small businesses aiming to improve their online presence and attract more customers. By implementing effective strategies such as keyword research, on-page optimization, local SEO, and content marketing, businesses can increase website traffic and build credibility. Technical SEO ensures a smooth user experience, while link building strengthens authority. Mobile SEO is crucial as more users access the web via smartphones. Businesses must track key performance metrics using analytics to refine their strategies continuously. As digital trends evolve, SEO remains a powerful tool for long-term success. The benefits of digital marketing for small businesses are maximized when SEO is leveraged effectively.

TikTok hat sich in den letzten Jahren zu einer der dominierenden Social-Media-Plattformen weltweit entwickelt. Millionen von Nutzern weltweit teilen täglich ihre Videos und streben nach einer größeren Reichweite und mehr

Dogs are more than just pets; they are loyal companions, protectors, and beloved members of the family. Whether you’re a new dog owner or an experienced pet parent, investing in

Salesforce partners play a crucial role in helping businesses navigate the complexities of security frameworks, data protection laws, and compliance requirements. By leveraging their expertise, companies can ensure that their Salesforce environment is secure, properly configured, and fully compliant with the necessary regulations.




















Ranks rocket connects website owners with bloggers for free guest posting! Increase brand awareness and backlinks with strategic placements. But remember, quality content is key.