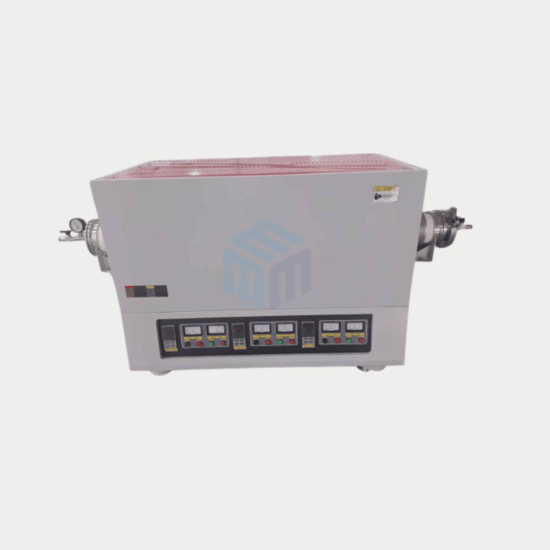
In any research facility, laboratory tube furnaces play a crucial role in heating, sintering, annealing, or material testing processes. These furnaces are designed to reach extremely high temperatures with precision and consistency. However, with great power comes great responsibility — maintaining and operating a high temperature tube furnace safely is vital to ensure reliable results, long equipment life, and the protection of lab personnel.
In this guide, we’ll explore essential lab safety practices and maintenance tips for tube furnaces, discuss the factors influencing the tube furnace price, and share insights on choosing the best tube furnace in India for your research needs.
Understanding Tube Furnaces and Their Role in the Laboratory
A tube furnace is a type of laboratory heating equipment used to conduct thermal processing in controlled atmospheres or vacuum conditions. It consists of a cylindrical heating chamber (usually made of alumina or quartz) that allows gases or samples to pass through while being uniformly heated.
These furnaces are widely used in:
- Material science and ceramics research
- Heat treatment of metals and alloys
- Semiconductor processing
- Catalytic testing and pyrolysis
- Thermal analysis and sintering applications
Modern laboratory tube furnaces offer precise temperature control up to 1800°C, programmable controllers, and robust insulation systems to ensure energy efficiency and accuracy.
⚙️ Key Features of a High-Temperature Tube Furnace
Before diving into safety and maintenance, let’s understand what makes a high temperature tube furnace stand out in a research lab.
- Advanced Temperature Controllers
Modern furnaces use digital PID or programmable temperature controllers for accurate heating and ramp rates. - High-Quality Heating Elements
Silicon carbide (SiC) or molybdenum disilicide (MoSi₂) elements ensure stable and efficient heating. - Superior Insulation Materials
Multi-layer ceramic fiber insulation minimizes heat loss and maintains thermal stability. - Versatile Tube Materials
The tube can be quartz, alumina, or inconel depending on the required temperature and chemical compatibility. - Compact Design for Lab Use
A lab tube furnace is typically benchtop-friendly, allowing easy installation and space management.
Essential Safety Guidelines for Operating Tube Furnaces
Safety should always be the first priority in a laboratory environment — especially when dealing with equipment capable of reaching temperatures above 1000°C. Below are key safety practices for tube furnace users.
1. Proper Installation and Setup
- Ensure your laboratory tube furnace is installed on a heat-resistant surface and has adequate ventilation.
- Keep the furnace away from flammable materials or liquids.
- Always connect it to a dedicated electrical circuit that can handle the load safely.
2. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
- Wear heat-resistant gloves, lab coats, and safety goggles while operating or opening the furnace.
- Use tongs or appropriate tools to handle hot samples and tubes.
3. Avoid Overloading
- Never exceed the manufacturer’s recommended load or temperature limit. Overloading may cause uneven heating and reduce the lifespan of the tube furnace.
4. Use Correct Tube Material
- Use the correct material (quartz, alumina, or steel) depending on the heating temperature and chemical nature of the sample to avoid tube cracking or contamination.
5. Ensure Safe Cooling
- Allow sufficient time for the furnace and samples to cool before handling. Forced cooling can cause thermal shock to the tube and heating elements.
6. Monitor Gas Flow and Pressure
- In gas atmosphere or vacuum setups, maintain appropriate gas flow and pressure levels. Leaks or incorrect flow can create unsafe environments or damage the furnace.
7. Routine Safety Checks
- Check power cables, thermocouples, and seals regularly. Any frayed wire or damaged sensor can lead to accidents or inaccurate temperature readings.
Maintenance Tips to Maximize Tube Furnace Life
A well-maintained high temperature tube furnace not only delivers consistent results but also reduces downtime and replacement costs. Here’s how you can keep your equipment in top condition.
1. Regular Cleaning
- Clean the exterior and accessible parts of the tube furnace periodically using a soft, dry cloth.
- Avoid using water or chemicals near heating zones or control panels.
- Clean the inner tube gently using a brush or vacuum (only when the furnace is cold).
2. Inspect Heating Elements
- Monitor the color, uniformity, and performance of SiC or MoSi₂ elements.
- Replace elements showing significant wear, sagging, or uneven heating.
3. Check Insulation Integrity
- Inspect ceramic fiber insulation for cracks or degradation. Damaged insulation can lead to energy loss and temperature instability.
4. Calibrate Temperature Controllers
- Regular calibration ensures accurate temperature readings and prevents overheating.
- Many research facilities schedule annual calibration for all lab tube furnaces.
5. Lubricate and Maintain Door Mechanisms
- If your furnace has hinged or sliding doors, ensure the mechanisms are smooth and properly aligned.
6. Prevent Tube Contamination
- Use protective liners or crucibles to avoid chemical reactions between samples and the furnace tube.
- Periodically replace the tube if it shows discoloration, pitting, or cracking.
Understanding Tube Furnace Price Factors
The tube furnace price varies depending on several specifications and design features. Understanding these factors helps researchers make informed purchases.
|
Factor |
Description |
|
Temperature Range |
Higher temperature (1200°C–1800°C) models cost more due to advanced materials and elements. |
|
Tube Material |
Quartz tubes are economical, while alumina and inconel tubes are more expensive but durable. |
|
Size and Design |
Larger or multi-zone tube furnaces cost more due to increased heating capacity. |
|
Controller Type |
Basic analog models are cheaper; digital and programmable units cost more but offer precision. |
|
Brand and Build Quality |
Reputable tube furnace manufacturers in India offer better warranty and service support. |
Choosing the Right Tube Furnace in India
If you are looking for a reliable tube furnace in India, consider the following points before purchase:
- Define Your Temperature Needs – Choose between 1100°C, 1400°C, or 1700°C depending on your research requirements.
- Check Energy Efficiency – Look for furnaces with low power consumption and efficient insulation.
- After-Sales Support – Ensure the supplier offers calibration, maintenance, and spare parts availability.
- Compare Tube Furnace Price and Warranty – A good balance between price, performance, and service ensures long-term satisfaction.
- Compliance and Safety Standards – Always choose equipment meeting international lab safety certifications.
Final Thoughts
Operating and maintaining a laboratory tube furnace requires diligence, precision, and respect for safety protocols. By following proper safety guidelines and maintenance practices, you can significantly extend the life of your high temperature tube furnace, ensure consistent experimental results, and create a safer laboratory environment.
Whether you are a research student or a lab manager, understanding the working principles and best practices of your lab tube furnace will help you get the most out of your investment — ensuring both performance and protection for years to come.