We value your privacy
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience, serve personalized ads or content, and analyze our traffic. By clicking "Accept All", you consent to our use of cookies.
We use cookies to help you navigate efficiently and perform certain functions. You will find detailed information about all cookies under each consent category below.
The cookies that are categorized as "Necessary" are stored on your browser as they are essential for enabling the basic functionalities of the site. ...
Necessary cookies are required to enable the basic features of this site, such as providing secure log-in or adjusting your consent preferences. These cookies do not store any personally identifiable data.
No cookies to display.
Functional cookies help perform certain functionalities like sharing the content of the website on social media platforms, collecting feedback, and other third-party features.
No cookies to display.
Analytical cookies are used to understand how visitors interact with the website. These cookies help provide information on metrics such as the number of visitors, bounce rate, traffic source, etc.
No cookies to display.
Performance cookies are used to understand and analyze the key performance indexes of the website which helps in delivering a better user experience for the visitors.
No cookies to display.
Advertisement cookies are used to provide visitors with customized advertisements based on the pages you visited previously and to analyze the effectiveness of the ad campaigns.
No cookies to display.
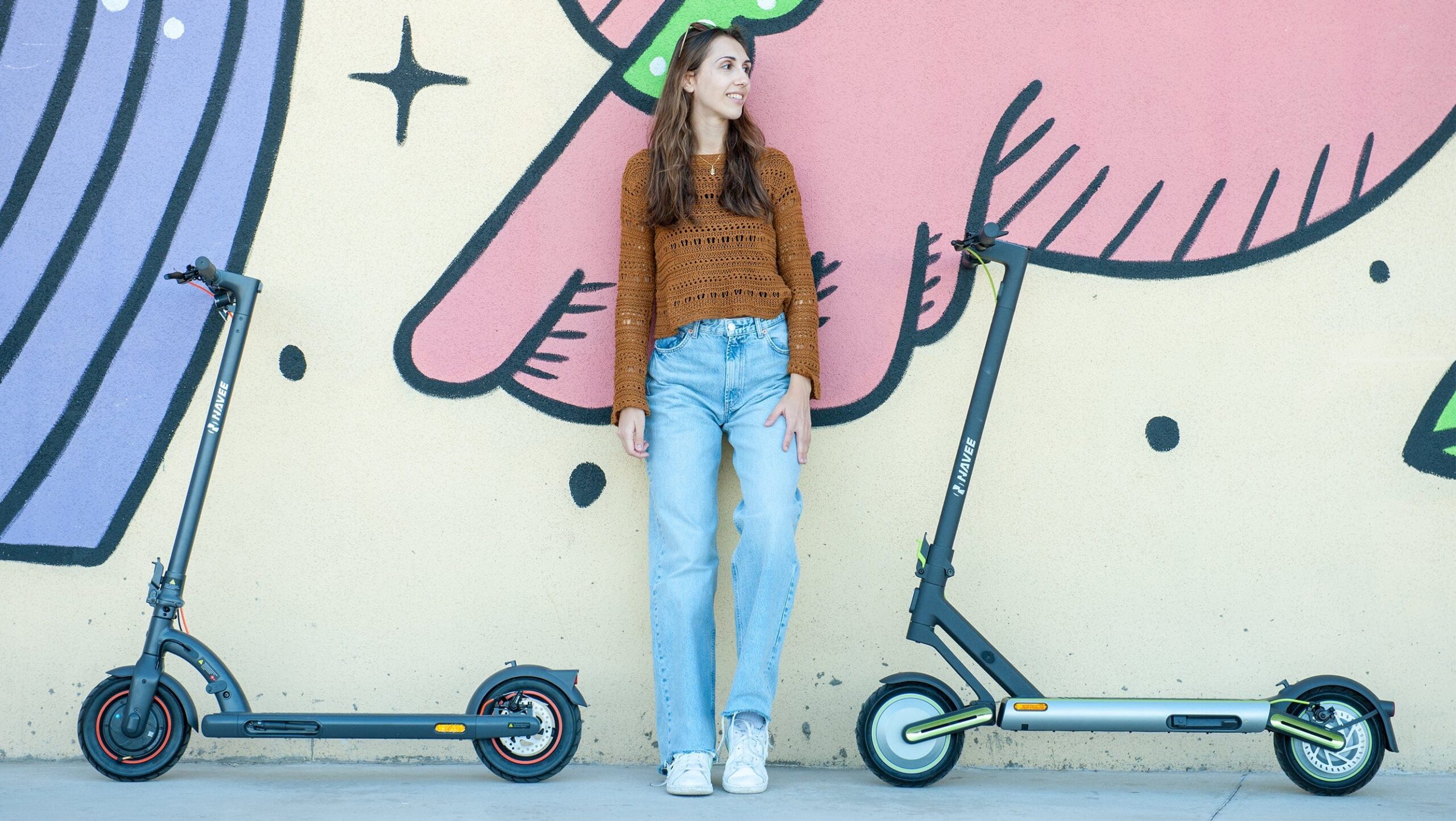

How the Navee Electric Scooter Changed My Commute for the Better
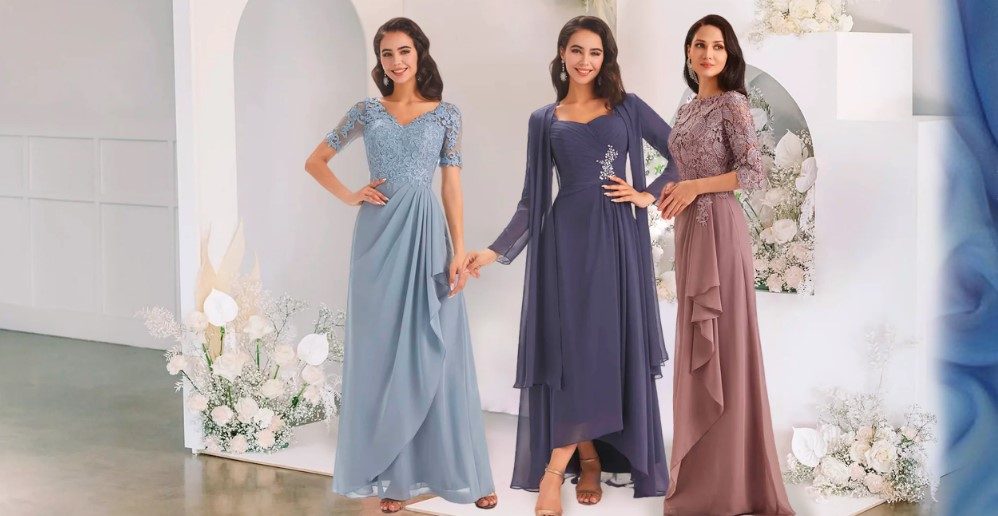

Desert Coral Bridesmaid Dresses: The Trending Color Brides Are Choosing in 2025

If you’re thinking about refreshing your home decor or just adding a light, breezy vibe to your windows, sheer curtains are a fantastic choice. And what’s even better? You can

Discover the key principles behind designing your dream home. Learn how an expert architect in Varanasi balances vision, function, and aesthetics to create personalized living spaces.

𝐎𝐯𝐞𝐫𝐯𝐢𝐞𝐰 The Global Composites Market Size was valued at USD 132.98 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach nearly USD 249.82 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 8.2% during

Rediscover your creativity. Enroll today and let your artistic journey begin at Brighton Recreational Centre—where community and creativity come together.

In the world of automotive restoration, few names resonate as profoundly as Danny Deerey. As the founder of Defenders-US, a Naples, Florida-based restoration company, Danny has redefined the art of

Discover why plain cargo overalls often outperform trendy workwear with superior durability, comfort, and professional utility.

Studying abroad is a dream for many Indian students, offering access to world-class education, global exposure, and a competitive edge in the job market. However, the cost of international education

In the extent of material science, where innovation pushes the boundaries of constant probability, acrylonitril separates beetroot stylin (ABS) plastic sheet as a remarkable versatile and durable material.
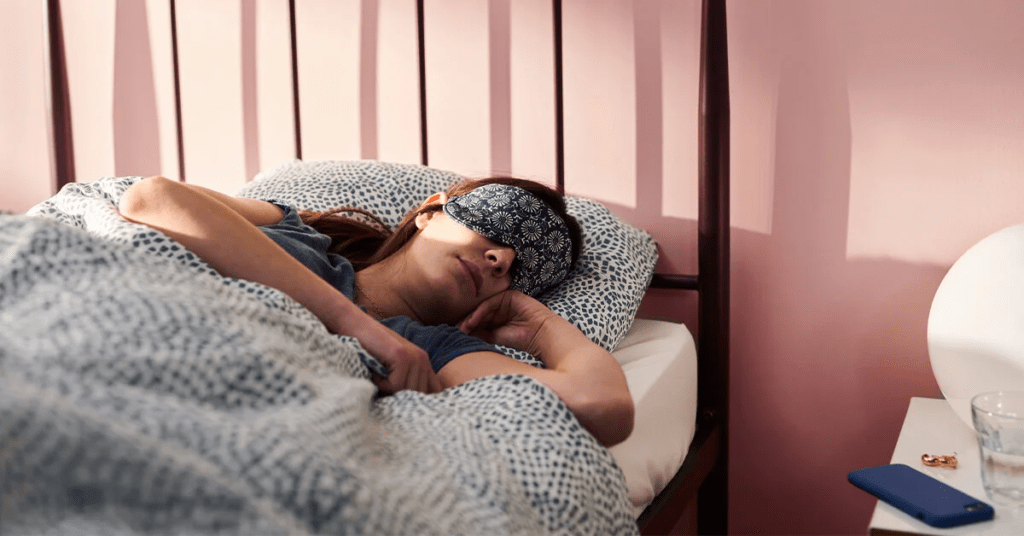

We’ve all heard the phrase “get your beauty sleep,” but for women, good sleep goes way beyond just looking refreshed. It’s a powerful regulator of hormones—those chemical messengers that control

Even as private enterprises, researchers, scientists and governments together try to prepare us for a brighter, safer, healthier and happier future, there has to be someone alleviating the suffering and
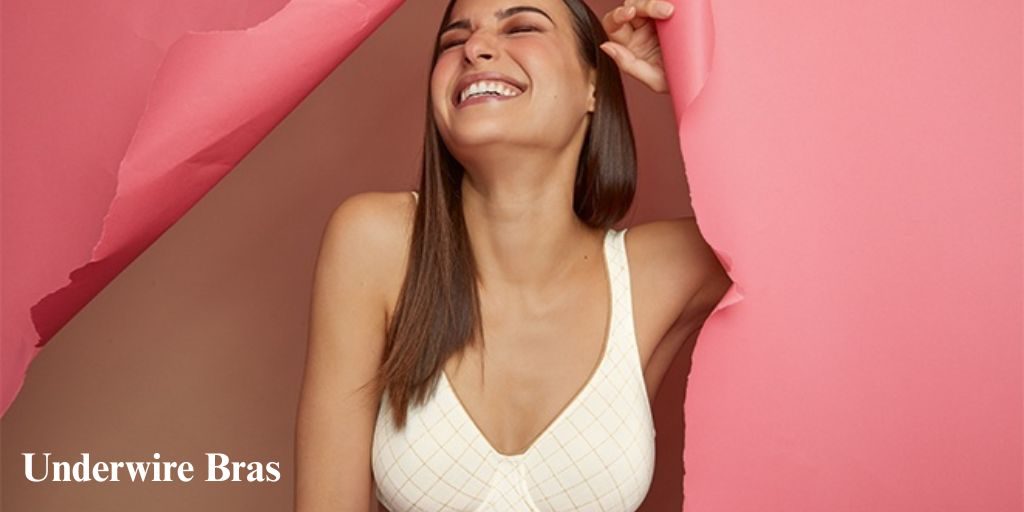

With over 135 years of experience Anita has become one of the world’s leading family-owned German heritage brands that is proud to continuously meet the various needs of women in all stages of their lives.

An MBA in Aviation Management is a specialised postgraduate programme designed to equip students with comprehensive knowledge and managerial skills tailored to the aviation and airport sectors. This course prepares students to address the dynamic challenges of the global aviation industry through a curriculum that blends theoretical learning with practical application. With a focus on strategic decision-making, operational efficiency, and regulatory compliance, the programme aims to develop future-ready professionals capable of leading in diverse aviation environments.

Texture in art refers to the surface quality or feel of an artwork, both visually and physically.

Explore how plastic manufacturing companies strengthen supply chain resilience through strategic planning, digitalization, and risk mitigation in polymer production.

The carbon credit market is an evolving mechanism designed to incentivize the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions by allowing entities to trade credits that represent the right to emit a specific amount of carbon dioxide or its equivalent.

Preparing for the CUET PG (Common University Entrance Test – Postgraduate) can be a challenging journey, especially with the increasing competition and pressure to secure a seat in a top
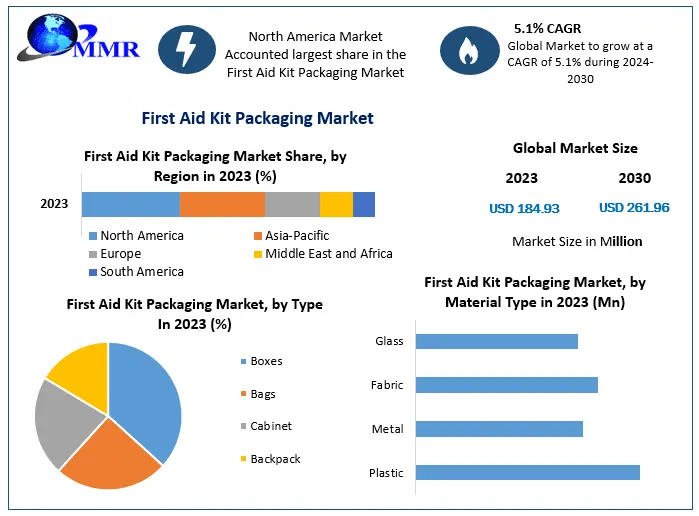
In terms of region, North America is expected to hold the largest share in the global market owing to strict government regulations regarding a safe workplace environment.

he blog “Design Every Room Right: Versatile Wallpaper That Fits All Spaces” highlights how choosing the right wallpaper can enhance every area of the home. It covers practical wallpaper ideas for kids’ rooms, nurseries, living rooms, home offices, bedrooms, bathrooms, hallways, and entryways.




















Ranks rocket connects website owners with bloggers for free guest posting! Increase brand awareness and backlinks with strategic placements. But remember, quality content is key.