We value your privacy
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience, serve personalized ads or content, and analyze our traffic. By clicking "Accept All", you consent to our use of cookies.
We use cookies to help you navigate efficiently and perform certain functions. You will find detailed information about all cookies under each consent category below.
The cookies that are categorized as "Necessary" are stored on your browser as they are essential for enabling the basic functionalities of the site. ...
Necessary cookies are required to enable the basic features of this site, such as providing secure log-in or adjusting your consent preferences. These cookies do not store any personally identifiable data.
No cookies to display.
Functional cookies help perform certain functionalities like sharing the content of the website on social media platforms, collecting feedback, and other third-party features.
No cookies to display.
Analytical cookies are used to understand how visitors interact with the website. These cookies help provide information on metrics such as the number of visitors, bounce rate, traffic source, etc.
No cookies to display.
Performance cookies are used to understand and analyze the key performance indexes of the website which helps in delivering a better user experience for the visitors.
No cookies to display.
Advertisement cookies are used to provide visitors with customized advertisements based on the pages you visited previously and to analyze the effectiveness of the ad campaigns.
No cookies to display.

Final Words Love is beautiful, confusing, and often unpredictable. But you don’t have to navigate it blindly. Whether you’re in love, healing from it, or curious about what’s next, Love Horoscope Daily offers guidance, not answers. Reflection, not rules. So light a candle. Ask a question. Pull a card. Whether it’s the quick truth of the Yes or No Tarot, the layered emotion in a 7 Card Spread, or the playful surprise of the Love Calculator, this platform helps you connect with the only voice that matters: your own.

Diabetes is often referred to as a “silent killer” because of its gradual impact on vital organs. It’s a condition that, if not monitored regularly, can lead to severe complications
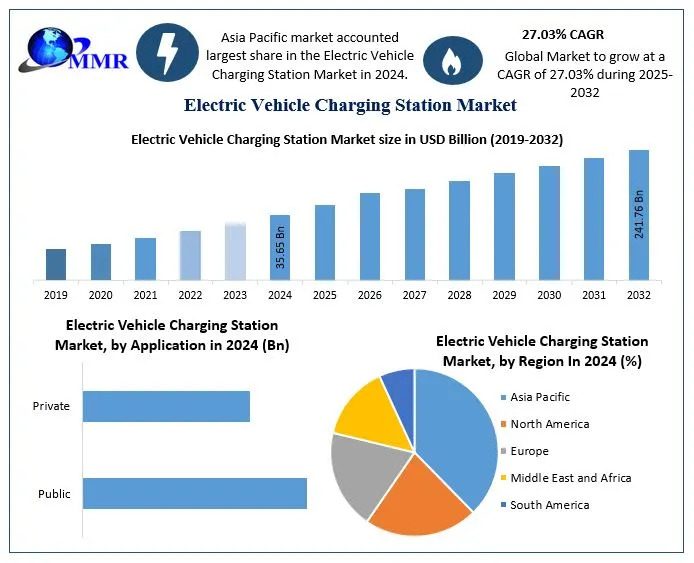
Global Electric Vehicle Charging Station Market to Surge to USD 241.76 Billion by 2032, Driven by Infrastructure Expansion and Strategic Collaborations The global Electric Vehicle Charging Station Market is poised for unprecedented growth,

In a world overwhelmed by options, “The Best of Everything” is not just a phrase, it is a mindset. This guide explores how choosing well across different areas of life can lead to more satisfaction, less waste, and a clearer sense of what truly matters. Whether it is about what you buy, how you travel, or how you spend your time, the pursuit of quality over quantity changes everything.

Discover the top 15 WordPress maintenance tasks that keep your website running smoothly.

Introduction to PP Glass-Lined Sheets Polypropylene (PP) glass-lined sheets are commonplace in many industries and applications requiring corrosion resistant and chemically inert materials, and are produced by glass being bonded

In a city that prides itself on going above and beyond, a Helicopter Tour Dubai is one of the best ways to see and appreciate its scale, beauty, and innovation.

Did you know Texas faces over 100 days of extreme heat each year? That kind of weather demands more than just basic construction.

The Dubai Safari Desert Tour is the perfect trip for you and your family! You’ll ride camels, drive dune buggies, enjoy the golden sand, and have so much fun.

Choosing new cabinets requires a thorough assessment of the ornamental and useful features meant to enhance your residence. Cabinets are more than simply basic storage areas since they greatly affect

Introduction: The Growing Demand for Sustainable Packaging In today's environmentally conscious world, businesses in all areas are looking for sustainable alternatives to packaging. Durable, breathable, and eco-friendly, leno mesh bags
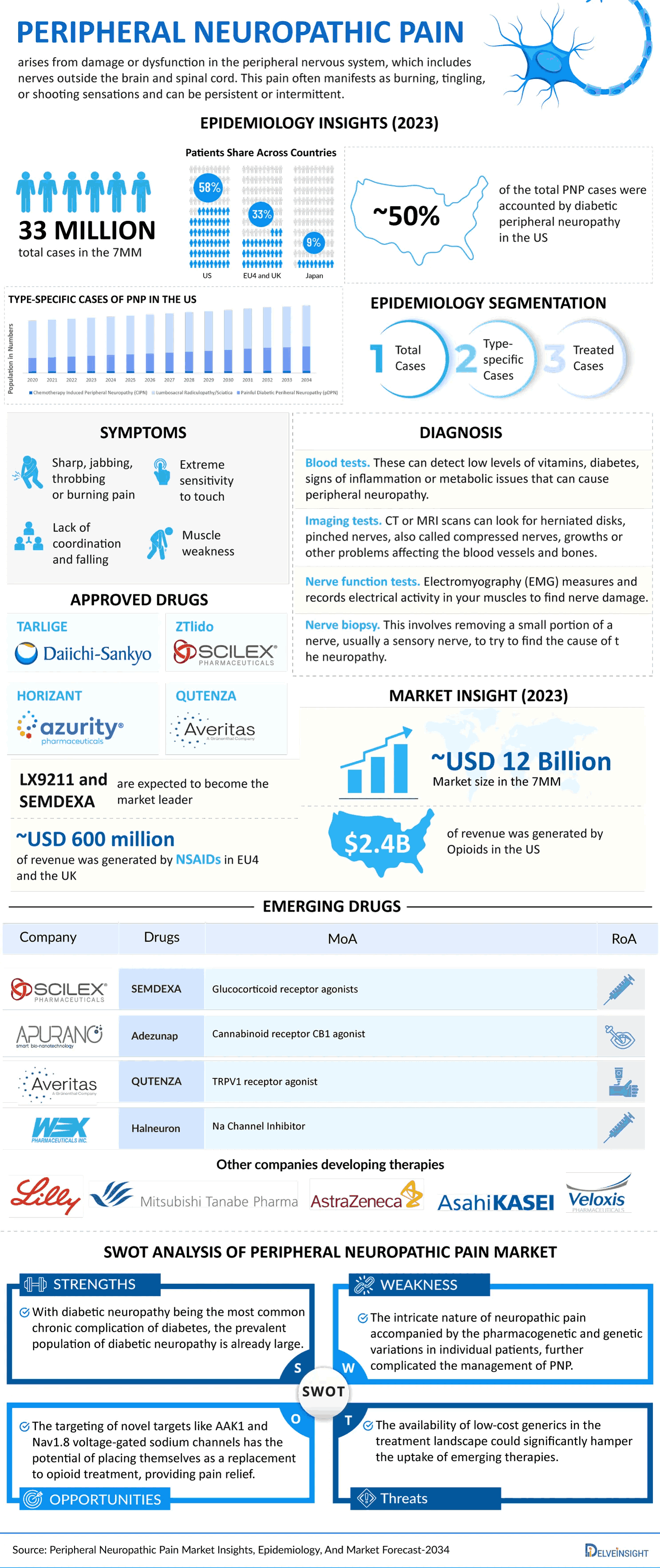
Peripheral Neuropathic Pain (PNP) arises from damage or dysfunction in the peripheral nervous system, which encompasses sensory, motor, and autonomic nerves outside the central nervous system. This condition can be

ArtWiki is your go-to resource for exploring the world of classical and modern art. Discover insightful articles on famous paintings, legendary artists, and diverse art styles. Whether you’re an enthusiast, student, or collector, ArtWiki helps you appreciate the stories and techniques behind history’s greatest masterpieces.

Looking for trusted ICSI Fertility treatment? Ekam Fertility, a leading IVF hospital in Hyderabad, offers advanced care, expert doctors, and personalized support for your parenthood journey.

Weighing a car loan vs. paying cash? Here’s a sharp look at the ups and downs of each option. Make the best call for your wallet and lifestyle.

Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight isn’t just about cutting calories or trying the latest diet trend. It’s about developing a long-term lifestyle focused on nourishing your body with the

Discover how a blockchain development company like LogicSpice can revolutionize your business operations with secure, transparent, and efficient blockchain solutions tailored to your industry.

The Indian financial market has witnessed an unprecedented rise in participation from individual investors, especially in the last decade. At the heart of this transformation is stock market trading—an exciting

Let’s take a step back in time, maybe to a quiet afternoon in a small Indian village or a bustling city street in the early hours. What’s one thing you’ll

Role of Texture in art refers to the surface quality of a work, encompassing both the physical feel and the visual appearance of an artwork.




















Ranks rocket connects website owners with bloggers for free guest posting! Increase brand awareness and backlinks with strategic placements. But remember, quality content is key.