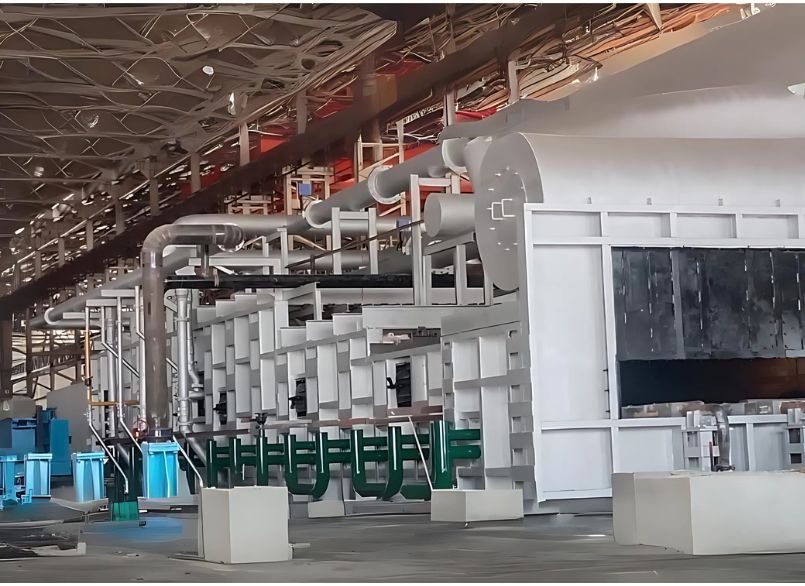
In the steel and metal processing industry, temperature control is everything. Before billets are rolled, forged, or shaped into finished products, they must be heated uniformly and precisely. This is where billet furnaces play a critical role. Designed to heat steel billets to the required rolling temperature, billet furnaces are essential in ensuring quality, productivity, and energy efficiency in rolling mills and forging plants.
This article explores how billet furnaces work, their types, key components, efficiency considerations, and best practices for modern steel manufacturing.
What Are Billet Furnaces?
Billet furnaces are industrial heating systems used to raise the temperature of steel billets to a uniform level before hot rolling or forging. Billets are semi-finished steel products, typically square or round in cross-section, that require reheating to temperatures between 1100°C and 1250°C depending on the steel grade and process requirements.
The primary goal of a billet furnace is to:
-
Ensure uniform heating throughout the billet
-
Reduce scale formation
-
Minimize fuel consumption
-
Maintain production speed
-
Preserve metallurgical properties
Proper billet heating directly impacts the quality of the finished steel product, surface finish, mechanical strength, and dimensional accuracy.
Why Billet Furnaces Are Important in Rolling Mills
In rolling mills, improperly heated billets can cause:
-
Surface cracks
-
Internal stresses
-
Uneven deformation
-
Increased rejection rates
A high-performance billet furnace ensures consistent heat penetration and controlled temperature distribution. This reduces defects and improves downstream processing efficiency.
Uniform heating also minimizes energy waste. Modern steel plants are increasingly focused on improving thermal efficiency to reduce operational costs and carbon emissions.
Types of Billet Furnaces
There are several types of billet furnaces used in steel plants, depending on production scale and plant layout.
1. Pusher Type Billet Furnace
In this system, billets are pushed through the furnace using hydraulic or mechanical pushers. It is widely used in medium and large rolling mills due to its simplicity and high throughput.
Advantages:
-
High production capacity
-
Continuous operation
-
Cost-effective for large-scale plants
2. Walking Beam Furnace
This advanced system uses a moving beam mechanism to transport billets through the furnace without physical dragging.
Advantages:
-
Minimal billet surface damage
-
Uniform heating
-
Reduced skid marks
-
Higher thermal efficiency
3. Rotary Hearth Furnace
Billets move in a circular path on a rotating hearth. This design allows uniform exposure to heat.
Advantages:
-
Compact design
-
Good temperature control
-
Suitable for specialized applications
Each type has its own benefits depending on production requirements, fuel availability, and plant design.
Key Components of a Billet Furnace
A well-designed billet furnace consists of multiple integrated components:
🔹 Combustion System
Includes industrial burners that mix fuel and air to generate controlled heat. Modern burners are designed for low emissions and stable flame control.
🔹 Refractory Lining
High-temperature refractory materials insulate the furnace and minimize heat loss while protecting the steel shell.
🔹 Heat Recovery System
Industrial recuperators or regenerative systems recover waste heat from exhaust gases and reuse it to preheat combustion air, improving efficiency.
🔹 Temperature Control System
Advanced automation ensures precise temperature monitoring across different zones of the furnace.
🔹 Charging and Discharging Mechanism
Mechanical systems ensure smooth billet movement without production delays.
Energy Efficiency in Billet Furnaces
Energy efficiency is one of the most important performance indicators for billet furnaces. Since reheating consumes a significant amount of fuel, even minor efficiency improvements can lead to substantial cost savings.
Ways to Improve Furnace Efficiency:
-
Installing waste heat recovery systems
-
Using high-efficiency industrial burners
-
Optimizing combustion air-to-fuel ratio
-
Maintaining proper refractory insulation
-
Implementing zone-based temperature control
According to energy management studies in industrial heating systems, proper waste heat recovery can improve thermal efficiency by up to 20–30%, depending on system design and operating conditions.
Efficient billet furnaces not only reduce fuel costs but also lower greenhouse gas emissions, helping industries move toward sustainable manufacturing.
Common Challenges in Billet Heating
Despite technological advancements, billet heating presents several operational challenges:
1. Scale Formation
Oxidation at high temperatures can cause scale buildup, affecting surface quality.
2. Uneven Heating
Poor temperature distribution can result in inconsistent mechanical properties.
3. High Fuel Consumption
Outdated furnace designs may consume excessive fuel.
4. Maintenance Downtime
Refractory wear and burner issues can cause production interruptions.
Regular inspection, proper calibration, and preventive maintenance are essential to minimize these issues.
Best Practices for Operating Billet Furnaces
To ensure long-term performance and efficiency, manufacturers should follow these best practices:
-
Conduct periodic burner tuning
-
Inspect refractory lining regularly
-
Monitor temperature uniformity across zones
-
Maintain proper billet spacing
-
Avoid overloading the furnace
-
Clean heat recovery systems to prevent blockage
Automation and digital monitoring systems also help track performance data in real time, allowing operators to make informed adjustments.
Technological Advancements in Modern Billet Furnaces
The steel industry is evolving rapidly, and billet furnace technology has advanced significantly in recent years.
🔹 Smart Control Systems
Modern furnaces integrate PLC and SCADA systems for automated temperature control and performance tracking.
🔹 Low-NOx Burners
Designed to reduce nitrogen oxide emissions while maintaining combustion efficiency.
🔹 Regenerative Burners
These burners use ceramic media to store and release heat, improving energy efficiency dramatically.
🔹 IoT Integration
Real-time monitoring of fuel consumption, temperature patterns, and maintenance alerts improves operational decision-making.
These innovations contribute to safer operations, lower operating costs, and better environmental compliance.
Environmental Considerations
Industrial heating processes are under increasing scrutiny due to environmental regulations. Billet furnaces must comply with emission norms related to:
-
Carbon dioxide (CO₂)
-
Nitrogen oxides (NOx)
-
Carbon monoxide (CO)
Using energy-efficient burners and recuperators significantly reduces environmental impact. Sustainable furnace design is no longer optional—it is a competitive necessity.
Choosing the Right Billet Furnace
When selecting a billet furnace, manufacturers should consider:
-
Production capacity
-
Fuel type availability
-
Energy efficiency ratings
-
Maintenance requirements
-
Automation level
-
Environmental compliance
A properly selected and engineered billet furnace improves product quality, reduces operational costs, and increases overall plant productivity.
Conclusion
Billet furnaces are the backbone of modern rolling mills and steel processing units. Their ability to deliver uniform heating, maintain metallurgical properties, and optimize energy usage directly impacts production quality and profitability.
As industries focus on efficiency and sustainability, advanced billet furnace designs incorporating heat recovery systems, smart controls, and low-emission burners are becoming the standard. Investing in a well-engineered billet furnace is not just about heating steel—it’s about improving performance, reducing costs, and ensuring long-term operational success.