Introduction
Agriculture has always been the backbone of human civilization, feeding billions and sustaining economies across the world. Yet, traditional farming is facing unprecedented challenges – climate change, resource scarcity, labor shortages, unpredictable weather, and the rising demand for higher food production. To address these issues, the agricultural sector is undergoing a remarkable digital transformation. Among the technologies driving this change, the Internet of Things (IoT) stands out as one of the most impactful innovations.
Definition
The Internet of Things (IoT) in agriculture refers to the use of connected sensors, devices, and smart technologies to monitor and manage farming operations in real time. By collecting data on soil conditions, weather, crop health, livestock activity, and equipment performance, IoT systems help farmers make more precise and efficient decisions, reduce waste, increase yields, and automate routine tasks.
What Is IoT in Agriculture?
IoT in agriculture involves using sensors, machines, drones, and other smart devices to monitor and manage farming operations. These devices communicate with each other and central software platforms, providing continuous data on soil conditions, crop health, weather patterns, livestock activity, and more.
Instead of relying solely on manual observation or traditional guesswork, farmers can now access precise, real-time insights. This shift empowers them to take immediate action—whether adjusting irrigation, treating pests, or predicting yields.
Key Applications of IoT in Agriculture
1. Precision Farming
Precision farming is the cornerstone of IoT-enabled agriculture. Sensors placed in fields measure soil moisture, nutrient levels, temperature, pH, and other critical factors. With this data, farmers can:
- Optimize the use of fertilizers
- Apply water only where needed
- Detect crop stress early
- Increase yields while lowering costs
Precision farming minimizes waste and enhances sustainability by ensuring resources are used efficiently.
2. Smart Irrigation Systems
Water scarcity is a major concern for farmers globally. IoT-powered irrigation systems use soil moisture sensors and weather data to determine the exact amount of water crops need. Automated drip or sprinkler systems then supply water only when necessary.
This reduces water usage by up to 30–50% and prevents issues like overwatering or waterlogging, which can damage crops.
3. Livestock Monitoring
IoT devices such as wearable sensors, smart tags, and GPS trackers help farmers monitor livestock health and behavior. These sensors can track:
- Body temperature
- Heart rate
- Movement patterns
- Feeding habits
If an animal is ill or injured, the system sends an instant alert. This allows for early intervention and helps reduce mortality rates. Additionally, GPS collars help track grazing patterns and prevent livestock theft.
4. Smart Greenhouses
Greenhouses equipped with IoT sensors can automatically regulate:
- Temperature
- Humidity
- Lighting
- CO₂ levels
Smart controllers adjust environmental conditions to ensure optimal plant growth. Farmers can manage their greenhouses remotely via mobile apps, improving efficiency and crop quality.
5. Drones and Aerial Monitoring
Drones play an increasingly important role in modern agriculture. They capture high-resolution images and monitor crop health through multispectral, thermal, and infrared sensors. With this data, farmers can:
- Detect diseases and pests early
- Assess irrigation performance
- Evaluate plant growth
- Plan field management
Drones significantly reduce labor and inspection time while providing more accurate field assessments.
6. Supply Chain and Logistics Monitoring
IoT improves agricultural supply chains by tracking the storage and transportation of produce. Smart containers and sensors maintain and monitor parameters such as:
- Temperature
- Humidity
- Vibration
- Location
This ensures freshness, reduces spoilage, and boosts transparency from farm to market.
Benefits of IoT in Agriculture
Higher Productivity with Data-Driven Decisions:
IoT provides accurate insights that help farmers make informed choices. From planting schedules to harvesting times, every decision becomes more precise, boosting crop yields and overall productivity.
Reduced Waste and Optimized Resource Usage:
By tailoring inputs such as water, fertilizers, and pesticides, IoT significantly reduces unnecessary waste. This leads to lower costs and protects the environment.
Improved Crop and Livestock Health:
Early detection of diseases and stress enables farmers to take timely action. Healthy plants and animals directly contribute to higher production and better quality.
Cost Savings Through Automation:
Automated irrigation, climate control, and monitoring reduce labor requirements and operational expenses.
Enhanced Sustainability:
Smart farming helps reduce carbon footprints, conserve water, and promote environmentally responsible agriculture.
Challenges of IoT Adoption in Agriculture
High Initial Investment:
IoT sensors, automated machines, drones, and software platforms can be expensive for small-scale farmers. However, costs are gradually decreasing as technology matures.
Limited Internet Access in Rural Areas:
Rural connectivity remains a challenge in many regions. Without reliable internet, IoT devices cannot transmit real-time data effectively.
Lack of Technical Knowledge:
Farmers need training to use IoT tools effectively. Governments and organizations must invest in skill development to support digital farming.
Data Privacy and Security Concerns:
The integration of smart devices increases the risk of cyber threats. Ensuring secure data transmission and storage is essential.
The Future of IoT in Agriculture
The future of agriculture lies in a fully integrated digital ecosystem where IoT works alongside AI, robotics, big data, and blockchain. Here are some emerging trends:
- AI-powered predictive analytics to forecast crop diseases and weather anomalies
- Autonomous tractors and robots for planting, spraying, and harvesting
- Blockchain-enabled traceability for full transparency in food supply chains
- 5G connectivity enabling faster data transmission and real-time control
As global populations grow and food demand increases, IoT will play a critical role in ensuring food security, sustainability, and profitability for farmers worldwide.
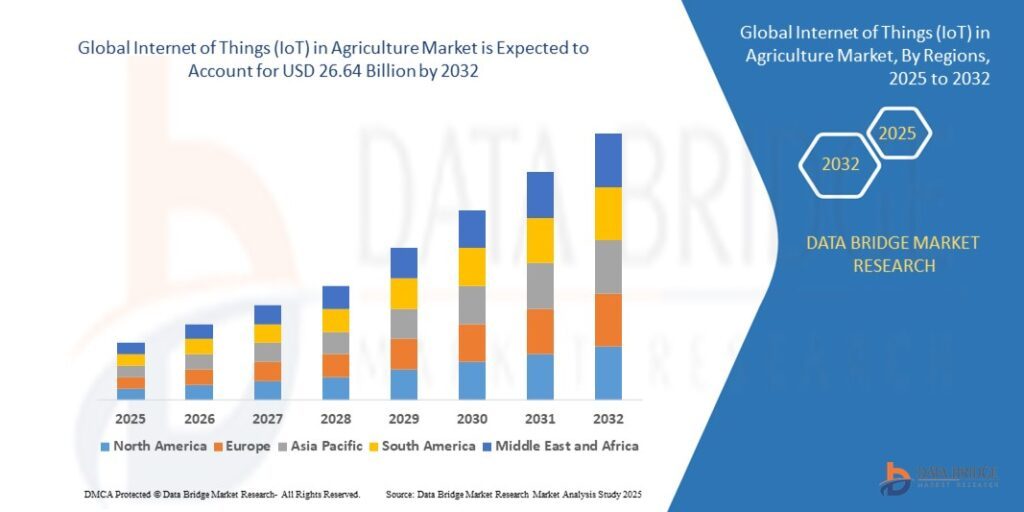
Growth Rate of Internet Of Things (Iot) In Agriculture Market
According to Data Bridge Market Research, the internet of things (IoT) in agriculture market was estimated to be worth USD 8.07 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 16.1% to reach USD 26.64 billion by 2032.
Learn More: https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-internet-of-things-iot-in-agriculture-market
Conclusion
The Internet of Things is revolutionizing agriculture, transforming traditional practices into efficient, data-driven systems. From precision farming to smart irrigation, livestock monitoring to automated greenhouses, IoT empowers farmers with unprecedented control and efficiency. While challenges such as cost and connectivity remain, the long-term benefits far outweigh them.